31
2025
-
03
Exploring the Different Materials Used in Stabilizer Bar Links for Enhanced Vehicle Stability
Exploring the Different Materials Used in Stabilizer Bar Links
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Stabilizer Bar Links
- 2. The Function of Stabilizer Bar Links
- 3. Common Materials Used in Stabilizer Bar Link Construction
- 3.1 Steel: The Traditional Choice
- 3.2 Aluminum: The Lightweight Alternative
- 3.3 Composite Materials: A Modern Approach
- 3.4 Rubber Components: The Unsung Heroes
- 4. How Material Choice Affects Performance
- 5. Durability and Longevity of Stabilizer Bar Links
- 6. Considerations for Installation and Replacement
- 7. Safety Implications of Material Selection
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions
- 9. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Stabilizer Bar Links
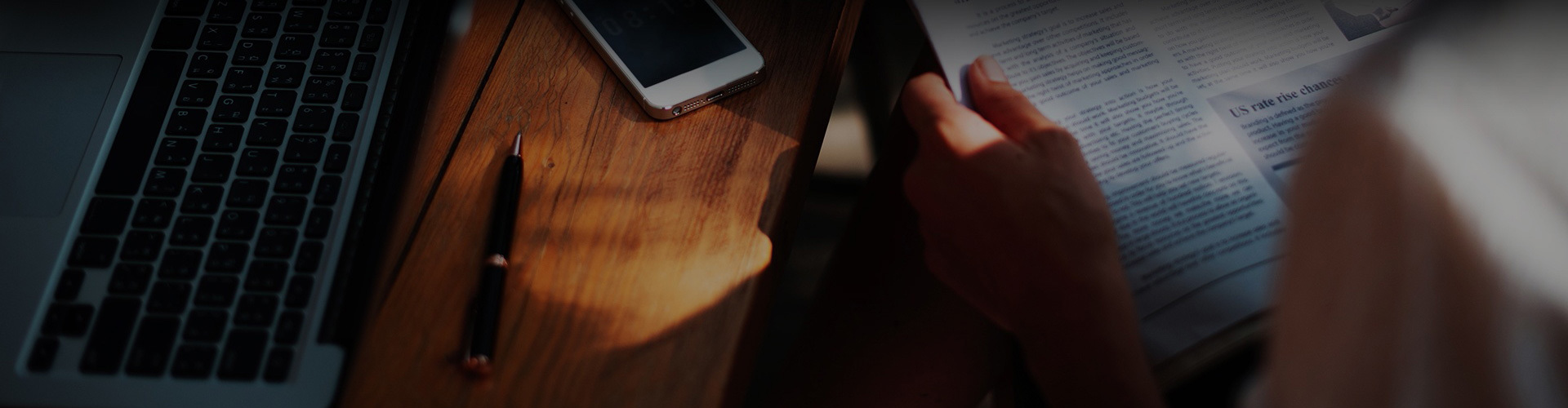
Stabilizer bar links, often referred to as sway bar links, play a pivotal role in a vehicle's suspension system. They connect the stabilizer bar (sway bar) to the suspension components, ensuring that the vehicle maintains balance and stability during cornering and sudden maneuvers. The construction of these links significantly impacts their effectiveness and overall vehicle performance. This article explores the various materials used in stabilizer bar links, helping vehicle owners understand their options for enhanced performance and safety.
2. The Function of Stabilizer Bar Links
The primary function of stabilizer bar links is to reduce body roll and improve vehicle handling. By connecting the sway bar to the left and right suspension, these links help distribute weight evenly across the vehicle. When a car turns, the stabilizer bar twists, allowing it to counteract the centrifugal forces acting on the vehicle. Without effective stabilizer bar links, drivers would experience greater body roll, resulting in less control and increased risk of accidents.
3. Common Materials Used in Stabilizer Bar Link Construction
The choice of material for stabilizer bar links has a direct effect on their performance, weight, and lifespan. Several materials are commonly used in the production of these critical components.
3.1 Steel: The Traditional Choice
Steel remains the most widely used material for stabilizer bar links due to its strength and durability. Steel links are resistant to bending and provide excellent performance under high-stress conditions. They can handle the forces exerted during sharp turns and rough driving conditions, making them a reliable choice for many vehicles.
3.2 Aluminum: The Lightweight Alternative
Aluminum has gained popularity as a lightweight alternative to steel. While it may not have the same tensile strength as steel, aluminum stabilizer bar links can significantly reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, improving fuel efficiency and handling. Additionally, aluminum is resistant to corrosion, making it an excellent option for vehicles that frequently encounter harsh weather conditions.
3.3 Composite Materials: A Modern Approach
Composite materials, including various plastics and reinforced materials, are increasingly being used in the production of stabilizer bar links. These materials offer a unique combination of lightweight properties and adequate strength. Composites can absorb vibrations and reduce noise, enhancing the overall ride quality. However, their long-term durability is still under scrutiny as they may not withstand extreme conditions as effectively as metal counterparts.
3.4 Rubber Components: The Unsung Heroes
While rubber isn't typically used as the main material for stabilizer bar links, it plays a crucial role in the bushings that connect these links to the suspension. Rubber bushings provide flexibility and dampening, which helps absorb shocks and vibrations, extending the life of the stabilizer bar links. Quality rubber components are essential for maintaining the functionality of the links and overall vehicle performance.
4. How Material Choice Affects Performance
The material used in stabilizer bar links directly influences vehicle performance. Steel links provide superior strength, making them ideal for performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications. Aluminum links offer a balance between weight-saving and strength, perfect for high-performance models that require agility. Composites can enhance ride comfort but may fall short in high-stress situations. **Choosing the right material based on driving conditions and vehicle type is crucial for optimizing performance.**
5. Durability and Longevity of Stabilizer Bar Links
Durability is a significant factor when considering stabilizer bar links. Steel links generally exhibit excellent longevity, particularly in standard driving conditions. However, they may be prone to rust if not properly coated. Aluminum links, while resistant to corrosion, may develop fatigue over time, especially under extreme stress.
Composite materials, while innovative, may degrade faster than metals, especially if exposed to UV rays or harsh chemicals. The longevity of rubber components can also be influenced by environmental factors, necessitating regular inspections and replacements to ensure optimal performance.
6. Considerations for Installation and Replacement
When installing or replacing stabilizer bar links, it's crucial to consider the choice of material as it affects the fit, compatibility, and performance of the vehicle. **Opting for high-quality materials and components during replacement ensures that the stabilizer bar links function effectively.** Professional installation is recommended to prevent issues related to improper alignment and torque settings.
7. Safety Implications of Material Selection
The choice of material for stabilizer bar links directly impacts vehicle safety. Weakened or degraded links can lead to increased body roll, reduced steering response, and compromised handling. It's essential to prioritize materials known for their reliability and strength, particularly for vehicles used in demanding driving conditions. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn links can prevent accidents and ensure the vehicle operates within safe parameters.
8. Frequently Asked Questions
What are stabilizer bar links?
Stabilizer bar links connect the stabilizer bar (sway bar) to the suspension system of a vehicle, helping to reduce body roll and improve handling during turns.
How often should stabilizer bar links be replaced?
It is recommended to inspect stabilizer bar links during routine maintenance and replace them every 50,000 to 100,000 miles, or sooner if signs of wear or damage are evident.
Can I replace stabilizer bar links myself?
Yes, with the right tools and knowledge, stabilizer bar links can be replaced at home. However, if you are unfamiliar with vehicle maintenance, it is advised to seek professional assistance.
What are the signs of worn stabilizer bar links?
Common signs of worn stabilizer bar links include clunking noises during turns, excessive body roll, and a noticeable decrease in handling performance.
Do different materials affect the cost of stabilizer bar links?
Yes, the material used significantly impacts the cost. Steel links are typically more affordable, while aluminum and composite options may be pricier due to their specialized properties.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the various materials used in stabilizer bar links is crucial for vehicle owners seeking to optimize performance and safety. Each material offers unique advantages and disadvantages, influencing factors such as durability, weight, and overall vehicle handling. By making informed decisions based on driving conditions and vehicle specifications, one can ensure that their stabilizer bar links function effectively, enhancing the safety and driving experience. Regular maintenance and timely replacements will help keep your vehicle in top shape, providing peace of mind on every journey.
Related news